Pakistan
CJP-led bench takes up pleas challenging SC bill today amid PBC boycott
Published
3 years agoon
By

- Three petitions filed under Article 184(3) to set aside the bill.
- 8-member bench is headed by CJP Umar Ata Bandial.
- None of the judges who questioned CJP powers included in bench.
ISLAMABAD: An eight-member bench of the Supreme Court will take up three petitions challenging the Supreme Court (Practice and Procedure) Bill 2023 amidst a boycott of court proceedings by the country’s top lawyers body in protest “against fixation of pleas in haste”.
A late-night announcement, made by PBC Vice Chairman Haroonur Rashid and Executive Committee Vice Chairman Hassan Raza Pasha, said that the chief justice constituted the bench in haste for hearing the petitions.
They said that the lawyers’ community would boycott the court proceedings across the country on Thursday.
Earlier this week, the bill — clipping CJP powers — was passed by a joint sitting of parliament after President Dr Arif Alvi returned it.
Subsequently, three separate petitions were filed by Raja Amer Khan, Chaudhry Ghulam Hussain and Mohammad Shafay Munir, among others, under Article 184(3) of the Constitution, asking the top court to set aside the bill.
The bench will be headed by Chief Justice of Pakistan (CJP) Umar Ata Bandial and comprises Justice Ijaz ul Ahsan, Justice Munib Akhtar, Justice Sayyed Mazahar Ali Akbar Naqvi, Justice Muhammad Ali Mazhar, Justice Ayesha Malik, Justice Syed Hasan Azhar Rizvi and Justice Shahid Waheed.
None of the judges who raised questions on the powers of the CJP have been included in the bench.
The petitions will be heard at 11:30am, according to the supplementary cause list uploaded on the Supreme Court website.
The bill has also been challenged in the Islamabad High Court (IHC) by lawyer Saeed Aftab in a separate plea.
The federal government got the bill passed in a joint session of parliament on Monday after President Arif Alvi returned it last week without signing it.
The president had returned the bill to parliament for reconsideration, citing Article 75 of the Constitution, and stating that its prima-facie travels beyond the competence of parliament and can be assailed as colourable legislation.
During the chaotic joint sitting, the house approved an amendment to the SC bill, under which a judges’ committee meeting would be convened to devise rules and regulations regarding the suo motu matters. The amendment was proposed by PML-N lawmaker Shaza Fatima Khawaja.
As per the amendment, the chief justice of Pakistan or any other member of the committee can call the meeting until the rules and regulations are finalised.
The bill
The Supreme Court (Practice and Procedure) Bill, 2023 aims to give the power of taking suo motu notice to a three-member committee comprising senior judges, including the chief justice. It also aims to have transparent proceedings in the apex court and includes the right to appeal.
Regarding the formation of benches, the bill states that every cause, matter or appeal before the apex court would be heard and disposed of by a bench constituted by a committee comprising the CJP and the two senior-most judges. It added that the decisions of the committee would be taken by a majority.
Regarding the apex court’s original jurisdiction, the bill said that any matter invoking the use of Article 184(3) would first be placed before the committee.
The bill says that if the committee is of the view that a question of public importance with reference to the enforcement of any of the fundamental rights conferred by Chapter I of Part II of the Constitution is involved, it shall constitute a bench comprising not less than three judges of the SC which may also include the members of the committee, for adjudication of the matter.
On matters where the interpretation of the Constitution is required, the bill said the committee would compose a bench comprising no less than five apex court judges for the task.
Regarding appeals for any verdict by an apex court bench that exercised jurisdiction under Article 184(3), the bill said that the appeal would have to be filed within 30 days of the bench’s order for a larger SC bench. It added that the appeal would be fixed for hearing within a period not exceeding 14 days.
It added that this right of appeal would also extend retrospectively to those aggrieved persons against whom an order was made under Article 184(3) prior to the commencement of the SC (Practice and Procedure) Bill, 2023 on the condition that the appeal was filed within 30 days of the act’s commencement.
The bill additionally said that a party would have the right to appoint its counsel of choice for filing a review application under Article 188 of the Constitution.
Furthermore, it states that an application pleading urgency or seeking interim relief, filed in a cause, appeal or matter, shall be fixed for hearing within 14 days from the date of its filing.
The bill said that its provisions would have effect notwithstanding anything contained in any other law, rules, or regulations for the time being in force or judgement of any court, including the Supreme Court and high courts.
You may like

In a unanimous verdict, a five-member bench of the Supreme Court on Monday declared civilians’ trials in military courts null and void as it admitted the petitions challenging the trial of civilians involved in the May 9 riots triggered by the arrest of Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) chief Imran Khan in a corruption case.
The five-member apex court bench — headed by Justice Ijaz Ul Ahsan, and comprising Justice Munib Akhtar, Justice Yahya Afridi, Justice Sayyed Mazahar Ali Akbar Naqvi and Justice Ayesha Malik — heard the petitions filed by the PTI chief and others on Monday.
The larger bench in its short verdict ordered that 102 accused arrested under the Army Act be tried in the criminal court and ruled that the trial of any civilian if held in military court has been declared null and void.
The apex court had reserved the verdict earlier today after Attorney General of Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan completed his arguments centred around the domain and scope of the military courts to try the civilians under the Army Act.
At the outset of the hearing today, petitioner lawyer Salman Akram Raja told the bench that trials of civilians already commenced before the top court’s verdict in the matter.
Responding to this, Justice Ahsan said the method of conducting proceedings of the case would be settled after Attorney General of Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan completed his arguments.
Presenting his arguments, the AGP said he would explain to the court why a constitutional amendment was necessary to form military courts in 2015 to try the terrorists.
Responding to Justice Ahsan’s query, AGP Awan said the accused who were tried in military courts were local as well as foreign nationals.
He said the accused would be tried under Section 2 (1) (D) of the Official Secrets Act and a trial under the Army Act would fulfill all the requirements of a criminal case.
“The trial of the May 9 accused will be held in line with the procedure of a criminal court,” the AGP said.
The AGP said the 21st Amendment was passed because the terrorists did not fall in the ambit of the Army Act.
“Amendment was necessary for the trial of terrorists [then] why amendment not required for the civilians? At the time of the 21st constitutional amendment, did the accused attack the army or installations?” inquired Justice Ahsan.
AGP Awan replied that the 21st Amendment included a provision to try accused involved in attacking restricted areas.
“How do civilians come under the ambit of the Army Act?” Justice Ahsan asked the AGP.
Justice Malik asked AGP Awan to explain what does Article 8 of the Constitution say. “According to Article 8, legislation against fundamental rights cannot be sustained,” the AGP responded.
Justice Malik observed that the Army Act was enacted to establish discipline in the forces. “How can the law of discipline in the armed forces be applied to civilians?” she inquired.
The AGP responded by saying that discipline of the forces is an internal matter while obstructing armed forces from discharging duties is a separate issue.
He said any person facing the charges under the Army Act can be tried in military courts.
“The laws you [AGP] are referring to are related to army discipline,” Justice Ahsan said.
Justice Malik inquired whether the provision of fundamental rights be left to the will of Parliament.
“The Constitution ensures the provision of fundamental rights at all costs,” she added.
If the court opened this door then even a traffic signal violator will be deprived of his fundamental rights, Justice Malik said.
The AGP told the bench that court-martial is not an established court under Article 175 of the Constitution.
At which, Justice Ahsan said court martials are not under Article 175 but are courts established under the Constitution and Law.
After hearing the arguments, the bench reserved the verdict on the petitions.
A day earlier, the federal government informed the apex court that the military trials of civilians had already commenced.
After concluding the hearing, Justice Ahsan hinted at issuing a short order on the petitions.
The government told the court about the development related to trials in the military court in a miscellaneous application following orders of the top court on August 3, highlighting that at least 102 people were taken into custody due to their involvement in the attacks on military installations and establishments.
Suspects express confidence in mly courts
The same day, expressing their “faith and confidence” in military authorities, nine of the May 9 suspects — who are currently in army’s custody — moved the Supreme Court, seeking an order for their trial in the military court be proceeded and concluded expeditiously to “meet the ends of justice”.
Nine out of more than 100 suspects, who were in the army’s custody, filed their petitions in the apex court via an advocate-on-record.
The May 9 riots were triggered almost across the country after former prime minister Imran Khan’s — who was removed from office via a vote of no confidence in April last year — arrest in the £190 million settlement case. Hundreds of PTI workers and senior leaders were put behind bars for their involvement in violence and attacks on military installations.
Last hearing
In response to the move by the then-government and military to try the May 9 protestors in military courts, PTI Chairman Imran Khan, former chief justice Jawwad S Khawaja, lawyer Aitzaz Ahsan, and five civil society members, including Pakistan Institute of Labour Education and Research (Piler) Executive Director Karamat Ali, requested the apex court to declare the military trials “unconstitutional”.
The initial hearings were marred by objections on the bench formation and recusals by the judges. Eventually, the six-member bench heard the petitions.
However, in the last hearing on August 3, the then-chief justice Umar Ata Bandial said the apex court would stop the country’s army from resorting to any unconstitutional moves while hearing the pleas challenging the trial of civilians in military courts.
A six-member bench, led by the CJP and comprising Justice Ijaz Ul Ahsan, Justice Munib Akhtar, Justice Yahya Afridi, Justice Sayyed Mazahar Ali Akbar Naqvi, and Justice Ayesha Malik, heard the case.
In the last hearing, the case was adjourned indefinitely after the Attorney General for Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan assured the then CJP that the military trials would not proceed without informing the apex court.
Pakistan
Sea conditions ‘very high’ as Cyclone Tej moves towards northwestward
Published
2 years agoon
By
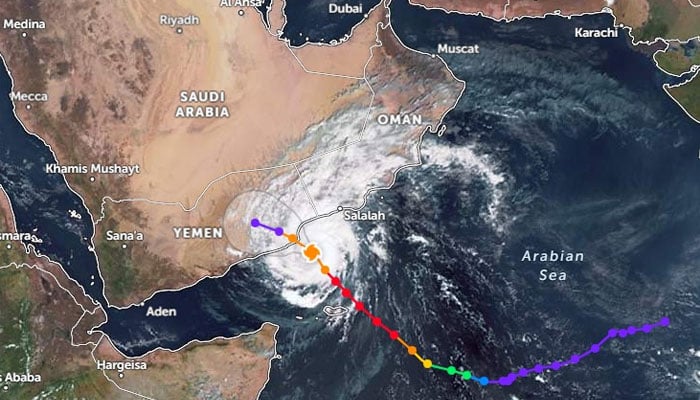
An Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm (ESCS) named “Tej”, which has been brewing in the southwest Arabian Sea for the past few days, has continued to move northwestward toward the Arabian Peninsula’s coast.
According to the Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD), over the past 12 hours, Cyclone Tej has been moving in a northwestward direction and is now “centred around latitude 14.4 N & longitude 53.2 °E”.
The update, which was issued today (Monday) at 10:00am (PST), also revealed that the brewing cyclone is situated “about 300km southwest of Salalah (Oman), 220km southeast of Al Ghaydah (Yemen) and 1520km southwest of Gwadar (Pakistan)”.
Additionally, the cyclone’s maximum sustained surface winds are between 150-160km/h, with gusts reaching 180km/h.
Moreover, sea conditions are currently very high, with maximum wave heights of 35ft around the system centre, according to the Met Office.
The system is expected to continue moving in a northwest direction and is likely to cross the Yemen coast, near Al Ghaydah by midnight as a very severe cyclonic storm (VSCS) with winds packing speeds of 120-130km/h and gusts reaching 150km/h.
However, it is important to note that there will be no impact on any of Pakistan’s coastal areas from this system.
According to PMD’s Daily Forecast, the weather is expected to remain dry for the next few days in most districts of Sindh, one of the coastal provinces of Pakistan.
Meanwhile, strong winds and thundershowers are likely to occur in and around some parts of Balochistan today, but dry weather is expected for the next few days.
Pakistan
PCB ‘dismisses’ objections over players support for Palestinians
Published
2 years agoon
By

LAHORE: Pakistan’s cricket team, which is currently busy participating in the ICC Men’s T20 Cricket World Cup, has shown their firm support and shared their prayers for all Palestinians suffering at the hands of Israel.
However, there have been many questions raised by Indian fans and cricket experts on the players’ constant support for Palestine asking ICC — the governing body of the game — whether such moves were allowed in the tournament.
According to sources, the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB) rejected the objections over players’ conduct saying: “The team’s expression of solidarity was a personal decision.”
Pakistan’s national team on Wednesday, posted a picture of the Palestinian flag on their individual X, formerly known as Twitter, accounts to show that they stand in solidarity with Palestine and that they are praying for the people suffering there including children.
☮️ ☮️ ☮️ ☮️ pic.twitter.com/r8E31Jsfya
— Shadab Khan (@76Shadabkhan) October 18, 2023
— Haris Rauf (@HarisRauf14) October 18, 2023
🤲🤲🤲🤲 pic.twitter.com/2hH4Gjmyhn
— Muhammad Nawaz (@mnawaz94) October 18, 2023
Prior to this Pakistan’s wicket-keeper batsman, Mohammad Rizwan, dedicated the team’s victory over Sri Lanka to his “brothers and sisters in Gaza”.
This was for our brothers and sisters in Gaza. 🤲🏼
— Muhammad Rizwan (@iMRizwanPak) October 11, 2023
Happy to contribute in the win. Credits to the whole team and especially Abdullah Shafique and Hassan Ali for making it easier.
Extremely grateful to the people of Hyderabad for the amazing hospitality and support throughout.
Meanwhile, Indian fans and cricket experts used the team’s support for Palestine to create controversies, claiming that the national team had violated ICC rules.
Sources from PCB added that the team is “allowed to express whatever they wanted to,” and that the players “did not violate any code of conduct by the ICC or PCB”.
The Health Ministry in Gaza reports that at least 3,061 Palestinians have died and over 13,750 more have been injured as a result of Israel’s shelling.
Pakistan has categorically condemned the Israeli atrocities and called for an immediate cessation of the bombardment, which has not even spared hospitals or schools, in solidarity with its Palestinian brothers and sisters.
Even Pakistani cricket legends who are not participating in the team anymore showed their support for Palestine.
🤲🏻🤲🏻 pic.twitter.com/8i20CX2Hka
— Kamran Akmal (@KamiAkmal23) October 18, 2023
#FreePalestine pic.twitter.com/IHC74YsxQH
— Zia Ul Haq (@zuh_leftarmfast) October 18, 2023
Moreover, Pakistan is set to face Australia tomorrow (Friday) in M Chinnaswamy Stadium, Bengaluru after a few days of rest.


Supreme Court annuls trials of civilians in military courts

Sea conditions ‘very high’ as Cyclone Tej moves towards northwestward

IMF condition: ECC set to green light gas tariff hike today

Barwaan Khiladi: Kinza Hashmi discusses her role as Alia

Snap launches tools for parents to monitor teens’ contacts

WATCH: Pakistani traveller deported from Dubai for damaging plane mid-air

Learn First | How to Create Amazon Seller Account in Pakistan – Step by Step

Sajjad Jani Funny Mushaira | Funny Poetry On Cars🚗 | Funny Videos | Sajjad Jani Official Team

