Business
October inflation eases to 23.8% in Pakistan
Published
3 years agoon
By

- Inflation number is in line with Ministry of Finance’s outlook.
- On a monthly basis, inflation moderates to 0.8% in November.
- Going forward, economist expects inflation to come down further.
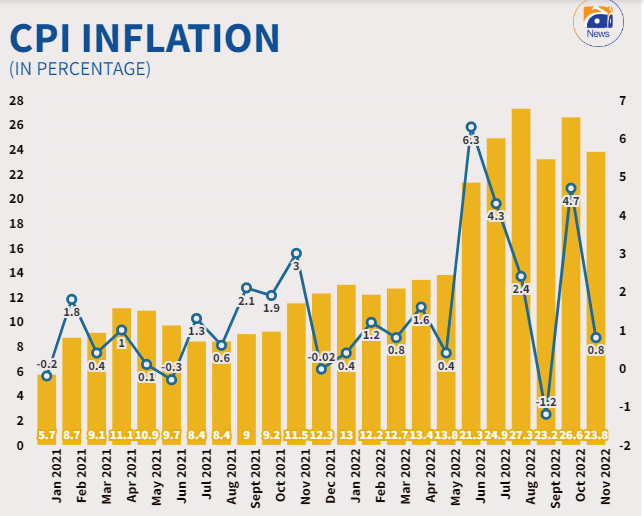
ISLAMABAD: The inflation rate eased to 23.8% last month compared to October’s record high inflation of 26.6% in line with the Ministry of Finance’s monthly outlook as the high base effect kicked in.
The latest inflation bulletin from the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS) also showed that the pace of price hikes also slowed down to 21.6% and 27.2% in urban and rural areas; however, the constant double-digit inflation in the country has adversely affected people’s purchasing power.
On a month-on-month basis, inflation moderated to 0.8% in November, compared to a whopping increase of 4% in the previous month and 3% in November 2021.
Economist Sana Tawfiq, while speaking to Geo.tv, cited a lower jump in food prices as a significant reason behind this month-on-month decline.
“Reasons for month-on-month moderation was lower jump in food prices with food index up meagre 0.1%, also transportation was down 0.1%.
“On the contrary; housing, clothing and household equipment indices were up monthly basis mostly showing a jump in winter-related items such as woollen garments and dry fruits,” she added.
The Ministry of Finance in its monthly outlook report had mentioned that inflationary pressure was expected to ease marginally in November due to smooth domestic supplies, unchanged energy prices and a stable exchange rate.
The prices of both non-perishable increased last month. The food group prices surged nearly 28.92% in November in comparison with the same month a year ago. The PBS data, however, showed that the prices of perishable food items decreased by 0.27%.
On a year-on-year basis, the pace of food inflation eased to 29.7% in cities and declined to 33.5% in villages and towns last month, according to PBS.
Non-food inflation dropped to 16.4% in urban areas and 21.4% in rural areas compared to the same month last year, according to the national data collecting agency.
Core inflation — calculated after excluding food and energy goods — eased to 14.6% in urban areas. However, it increased to 18.5% in rural areas. Tawfiq expressed concern over elevated core inflation as the economist believes higher core inflation is “alarming”.
“We expect headline inflation to come down further going forward, supported by high base,” Tawfiq predicted.
Price of essential kitchen items
The prices of onions — an essential vegetable used in all households — were higher by over 34% last month compared to September, followed by a 14.79% increase in the rates of tea, and nearly 14.5% in various the price of potatoes and dry fruits, according to the PBS.
However, the prices of vegetables decreased in a range of 10-30%, chicken by 5.08%, and rates of various pulses by over 5%, according to PBS.
You may like
-


IMF condition: ECC set to green light gas tariff hike today
-


Govt to only finance important projects for provinces: SIFC
-


Current account deficit declines to $8 million in September
-


Gas tariff set to increase by up to 100%
-


Indian exporters fear Pakistan could seize control of basmati rice market
-


Pakistan ‘very comfortably’ placed to meet IMF targets, SBP chief assures global investors

In a unanimous verdict, a five-member bench of the Supreme Court on Monday declared civilians’ trials in military courts null and void as it admitted the petitions challenging the trial of civilians involved in the May 9 riots triggered by the arrest of Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) chief Imran Khan in a corruption case.
The five-member apex court bench — headed by Justice Ijaz Ul Ahsan, and comprising Justice Munib Akhtar, Justice Yahya Afridi, Justice Sayyed Mazahar Ali Akbar Naqvi and Justice Ayesha Malik — heard the petitions filed by the PTI chief and others on Monday.
The larger bench in its short verdict ordered that 102 accused arrested under the Army Act be tried in the criminal court and ruled that the trial of any civilian if held in military court has been declared null and void.
The apex court had reserved the verdict earlier today after Attorney General of Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan completed his arguments centred around the domain and scope of the military courts to try the civilians under the Army Act.
At the outset of the hearing today, petitioner lawyer Salman Akram Raja told the bench that trials of civilians already commenced before the top court’s verdict in the matter.
Responding to this, Justice Ahsan said the method of conducting proceedings of the case would be settled after Attorney General of Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan completed his arguments.
Presenting his arguments, the AGP said he would explain to the court why a constitutional amendment was necessary to form military courts in 2015 to try the terrorists.
Responding to Justice Ahsan’s query, AGP Awan said the accused who were tried in military courts were local as well as foreign nationals.
He said the accused would be tried under Section 2 (1) (D) of the Official Secrets Act and a trial under the Army Act would fulfill all the requirements of a criminal case.
“The trial of the May 9 accused will be held in line with the procedure of a criminal court,” the AGP said.
The AGP said the 21st Amendment was passed because the terrorists did not fall in the ambit of the Army Act.
“Amendment was necessary for the trial of terrorists [then] why amendment not required for the civilians? At the time of the 21st constitutional amendment, did the accused attack the army or installations?” inquired Justice Ahsan.
AGP Awan replied that the 21st Amendment included a provision to try accused involved in attacking restricted areas.
“How do civilians come under the ambit of the Army Act?” Justice Ahsan asked the AGP.
Justice Malik asked AGP Awan to explain what does Article 8 of the Constitution say. “According to Article 8, legislation against fundamental rights cannot be sustained,” the AGP responded.
Justice Malik observed that the Army Act was enacted to establish discipline in the forces. “How can the law of discipline in the armed forces be applied to civilians?” she inquired.
The AGP responded by saying that discipline of the forces is an internal matter while obstructing armed forces from discharging duties is a separate issue.
He said any person facing the charges under the Army Act can be tried in military courts.
“The laws you [AGP] are referring to are related to army discipline,” Justice Ahsan said.
Justice Malik inquired whether the provision of fundamental rights be left to the will of Parliament.
“The Constitution ensures the provision of fundamental rights at all costs,” she added.
If the court opened this door then even a traffic signal violator will be deprived of his fundamental rights, Justice Malik said.
The AGP told the bench that court-martial is not an established court under Article 175 of the Constitution.
At which, Justice Ahsan said court martials are not under Article 175 but are courts established under the Constitution and Law.
After hearing the arguments, the bench reserved the verdict on the petitions.
A day earlier, the federal government informed the apex court that the military trials of civilians had already commenced.
After concluding the hearing, Justice Ahsan hinted at issuing a short order on the petitions.
The government told the court about the development related to trials in the military court in a miscellaneous application following orders of the top court on August 3, highlighting that at least 102 people were taken into custody due to their involvement in the attacks on military installations and establishments.
Suspects express confidence in mly courts
The same day, expressing their “faith and confidence” in military authorities, nine of the May 9 suspects — who are currently in army’s custody — moved the Supreme Court, seeking an order for their trial in the military court be proceeded and concluded expeditiously to “meet the ends of justice”.
Nine out of more than 100 suspects, who were in the army’s custody, filed their petitions in the apex court via an advocate-on-record.
The May 9 riots were triggered almost across the country after former prime minister Imran Khan’s — who was removed from office via a vote of no confidence in April last year — arrest in the £190 million settlement case. Hundreds of PTI workers and senior leaders were put behind bars for their involvement in violence and attacks on military installations.
Last hearing
In response to the move by the then-government and military to try the May 9 protestors in military courts, PTI Chairman Imran Khan, former chief justice Jawwad S Khawaja, lawyer Aitzaz Ahsan, and five civil society members, including Pakistan Institute of Labour Education and Research (Piler) Executive Director Karamat Ali, requested the apex court to declare the military trials “unconstitutional”.
The initial hearings were marred by objections on the bench formation and recusals by the judges. Eventually, the six-member bench heard the petitions.
However, in the last hearing on August 3, the then-chief justice Umar Ata Bandial said the apex court would stop the country’s army from resorting to any unconstitutional moves while hearing the pleas challenging the trial of civilians in military courts.
A six-member bench, led by the CJP and comprising Justice Ijaz Ul Ahsan, Justice Munib Akhtar, Justice Yahya Afridi, Justice Sayyed Mazahar Ali Akbar Naqvi, and Justice Ayesha Malik, heard the case.
In the last hearing, the case was adjourned indefinitely after the Attorney General for Pakistan (AGP) Mansoor Usman Awan assured the then CJP that the military trials would not proceed without informing the apex court.

- Tariff may go up by 173% for non-protected domestic consumers.
- Petroleum Division to push for implementation of hike from Oct 1.
- Circular debt to increase by Rs15bn if hike implemented from today.
ISLAMABAD: The Economic Coordination Committee (ECC) will meet today (Monday) to green-light the plan to hike the gas tariff, a key part of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) conditions, including a zero hike in the gas circular debt for the ongoing financial year 2023-24, reported The News.
The government is likely to increase the local gas tariff up to 173% for non-protected domestic consumers, 136.4% for commercial, 86.4% for export and 117% for the non-export industry.
Since there is no budgeted subsidy for even domestic, commercial, and industrial sectors, the high-end consumers will provide cross-subsidies to low-end consumers.
The government’s failure to hike the gas prices from July 1 has forced it to incur a loss of Rs50 billion during the July-September in the gas sector. But the losses will be bridged when the government moves ahead with the increase in the gas tariff which would give enough monetary space to recover with the loss.
As per the publication, the IMF has been taken onboard on this point. It has been informed that the gas prices would be increased in such a manner that it would not increase the circular debt during this financial year, which right now stands at Rs2.9 trillion.
However, now the Petroleum Division will try to ensure that the gas tariff hike is implemented from October 1. If the government decides to implement the hike from today onwards then the circular debt would increase by Rs15 billion.
But there would be no increase in the gas tariff from January 1, 2024, a further gas tariff increase would be implemented as under the law, the review of gas prices is carried out bi-annually.
The cement sector will have to purchase the gas 193.3% higher than the current cost, making it the biggest bearer of the brunt, from 1,500 per MMBtu to Rs4,400 per MMBtu.
The CNG sector, will face the second-highest increase in gas tariff by 143.8% from Rs1,805 per MMBtu to Rs4,400.
If the hike is approved, then it means that cement prices will skyrocket and CNG will be much more expensive than petrol.
The government, however, does not plan on increasing the tariff for tandoors which would ensure that roti prices remain stable.
The summary prepared by the petroleum ministry that is to be pitched today in the ECC meeting shows it has not spared the four protected domestic consumer categories as ostensibly it has not proposed to increase their gas tariffs but hiked their monthly fixed charges from Rs10 to Rs400 per month.
More importantly, the Petroleum Division has also proposed to escalate the per month fixed charges for the first 4 non-protected domestic consumers by 117.4% to Rs1,000 from Rs460 per month from their gas tariffs increase by 50-150%. Also, to be increased are per month fixed charges for the remaining 4 non-protected domestic consumers, by 334.78%, to Rs2,000 from Rs460 per month part, increasing their gas tariff by 100%-173%.
The summary states that SNGPL will now offer a blend of natural gas and RLNG in a 20:80 ratio to non-export industry out of the estimated volumes for industrial consumers, both process and captive, as per petitions filed by SNGPL to OGRA for revenue determination.
The blend offered by the Sui companies shall be reviewed every quarter based on the availability of natural gas and RLNG. And SSGC shall offer a blend of NG and RLNG of 90:10 out of the estimated volumes for industrial consumers, both process and captive, as per petitions filed by SSGC to OGRA for revenue determination.
Coming to the export industry, the summary says that currently, there is a wide price disparity between the industry operating on SSGCL and SNGPL networks. Industry in the north (operating on the SNGPL network) consumes a 50:50 blend of indigenous and RLNG for 9 months (Mar to Nov) and 100% RLNG for 3 months (Dec-Feb), averaging to the current tariff of $9.6/MMBtu (Rs2,790) over the year.
On the other hand, process connections of the industry in the south (operating on SSGCL) are being charged at Rs1,100/MMBtu. SSGC has recently started a supply of blend in the proportion of 75:25 for captive use of gas, which approximates $5.9/MMBtu (Rs1,710).

- PSDP listed projects to be presented before CCER for review.
- Finance minister to chair CCER meeting upon return from Morocco.
- “Exercise to abandon provincial projects underway,” top official says.
ISLAMABAD: The Special Investment Facilitation Council (SIFC) has decided to only finance extremely important development projects in the provinces with 50% of funds allocated by the federal government and provinces each, The News reported.
The Planning Ministry has, meanwhile, identified all the Public Sector Development Programmes (PSDP) listed projects to be presented before the Cabinet Committee on Economic Revival (CCER) with its aims to scrap all such schemes and save Rs314 billion under the austerity drive.
Finance Minister Dr Shamshad Akhtar, following her return from Morocco where she is attending the annual meetings of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF), will be chairing the CCER meeting.
“The exercise to abandon the provincial nature projects from PSDP list is underway,” a top government official said on Thursday.
It was decided in the last SIFC’s Apex Committee meeting that development projects of provincial nature would only be executed in the future through the cost-sharing of 50%:50% of funds borne by both the Centre and provinces. “If the provincial government does not bear 50% cost on an equal basis, the Centre will not provide its share of funding,” another top official source confirmed while talking to The News.
One senior official said the decision had already been taken up by the Executive Committee of the National Economic Council (ECNEC). The SIFC’s Executive Committee is scheduled to meet early next week to undertake all spadework for tabling it before the apex committee under the chairmanship of Caretaker Prime Minister Anwar-ul-Haq Kakar in the coming weeks.
So far, the SIFC has remained unable to finalise much-awaited multi-billion dollar transactions for attracting investments but it is making all-out efforts to lure foreign investors in areas of mining, IT, agriculture, and others.
One of the future SIFC agendas for considering mechanisms for corporate farming lies on the table. Although some initial work was done during the tenure of late Gen (retd) Musharraf, still there is a need to undertake its basic framework in a detailed manner before striking pacts with international investors. However, it is critical to hire technical experts for drafting international agreements and steering the negotiations against the backdrop of several past agreements ending up in disputes due to a lack of technical capacity.
Meanwhile, different ministries/divisions have been directed to undertake steps under the austerity plans to ensure savings. The Ministry of Finance instructed all its wings and attached departments to review all the foreign visits and banned all those deemed necessary next week.


Supreme Court annuls trials of civilians in military courts

Sea conditions ‘very high’ as Cyclone Tej moves towards northwestward

IMF condition: ECC set to green light gas tariff hike today

Barwaan Khiladi: Kinza Hashmi discusses her role as Alia

Snap launches tools for parents to monitor teens’ contacts

WATCH: Pakistani traveller deported from Dubai for damaging plane mid-air

Learn First | How to Create Amazon Seller Account in Pakistan – Step by Step

Sajjad Jani Funny Mushaira | Funny Poetry On Cars🚗 | Funny Videos | Sajjad Jani Official Team

